Periodontal Treatments. Smile Bold.
Only for boundary-breakers .


Beyond the dentristy.
If you've ever lost a tooth or needed a replacement, you might have heard about Periodontal Treatments.
They are a popular solution that not only looks and feels like your natural teeth but also offers long-term benefits. In this page, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about periodontal Treatments in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Periodontal Treatment
Periodontal treatment aims to foster the healthy development of the tissues supporting the teeth while eliminating harmful bacteria. The intensity of periodontal therapy is closely linked to the concentration of Streptococcus mutans in the oral cavity. Early intervention in periodontal treatments prevents the disease from moving to a later stage.
If left untreated, bacteria that appear as yellow-coloured plaques on the teeth lead to gingivitis and subsequently to periodontitis, resulting in the patient losing the connective tissues associated with the tooth in the later stages. Untreated periodontitis eventually causes tooth loss. According to the ADA (American Dental Association) report, 60% of the collective loss of teeth in America in old age is due to untreated periodontal diseases.
Periodontal diseases are characterised by inflammation and infection of the gums, which in turn affect the bone and connective tissues surrounding the teeth. The first symptoms of these diseases are bleeding gums and bad breath. Over time, these diseases cause the gums to recede and pockets to form between the gums and teeth. The progression of periodontal diseases develops gradually as follows:
Stages of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease develops in two main stages:
-
Gingivitis:
Gingivitis is the first manifestation of periodontal disease. However, these diseases are not always caused by plaque. Hormonal changes, immune system issues, and the influence of various chemicals can contribute to the development of gingivitis. Gingivitis symptoms, including redness, swelling, and bleeding, are treated with a comprehensive tartar therapy.
-
Periodontitis:
Periodontitis represents the advancement of periodontal diseases affecting the gums and extending to the root of the tooth. The gums, usually a coral pink in healthy conditions, take on a dark red hue in instances of periodontitis.
Periodontitis can lead to gingival recession, root surface exposure, and ultimately result in tooth loss in later stages. As periodontitis leads to bone loss, it may necessitate bone augmentation treatment. Following the treatment, the patient should prioritise oral care and schedule dental visits biannually for monitoring.
Periodontal treatment alternatives differ based on the severity of the condition:
Scaling and Root Planing:
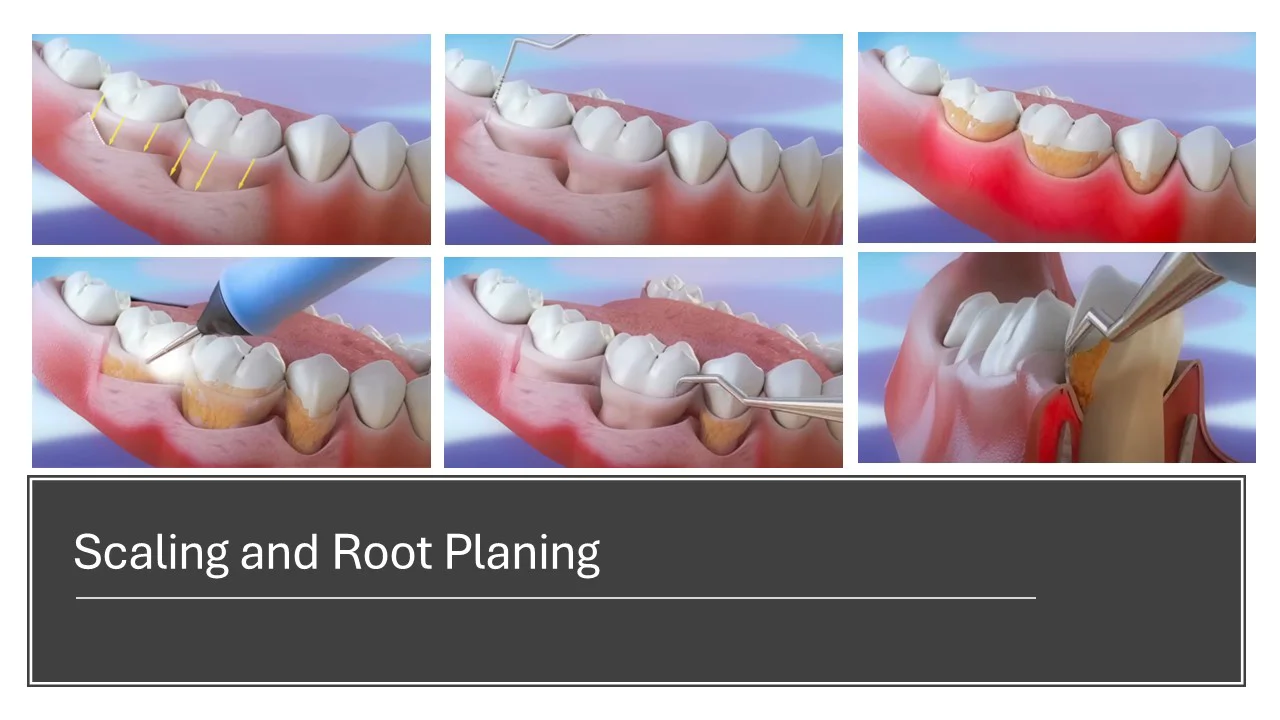
In periodontal treatments, the presence of plaques that infiltrate the gingival tissue and form periodontal pockets signifies that the disease has progressed to a subsequent stage, necessitating prompt intervention. In these instances, pocket depths are assessed utilising 'periodontal probes' that are manufactured in various thicknesses and types specific to each anatomical region. Subsequently, the removal of tartar and plaque is conducted with or without the incision of the gums at these specified depths.
Periodontal Surgery:
In certain instances, dental plaques may contribute to the resorption of bone in the gingival tissues and the roots of the teeth by migrating to the dental roots. In this case, bone augmentation procedures are implemented to rehabilitate the loss of bone in the affected area. The enhancement of bone density also yields beneficial results regarding the aesthetic appearance of the patient.
Laser Treatment:
Laser applications may be utilised independently in the treatment of periodontitis or may serve as a supplement to surgical interventions. In this methodology, laser beams are administered to the plaques via a slender probe. The application of laser beams produces minimised damage to healthy tissues compared to traditional surgical methods, consequently leading to diminished bleeding. Which substantially diminishes the likelihood of infectio
Gum diseases induced by plaque tend to disappear through the maintenance of proper oral hygiene. In instances where the pocket depth surpasses 4-5 mm, home treatment typically does not work. Only after a dental professional has evaluated the severity of their gingivitis can one understand this issue.
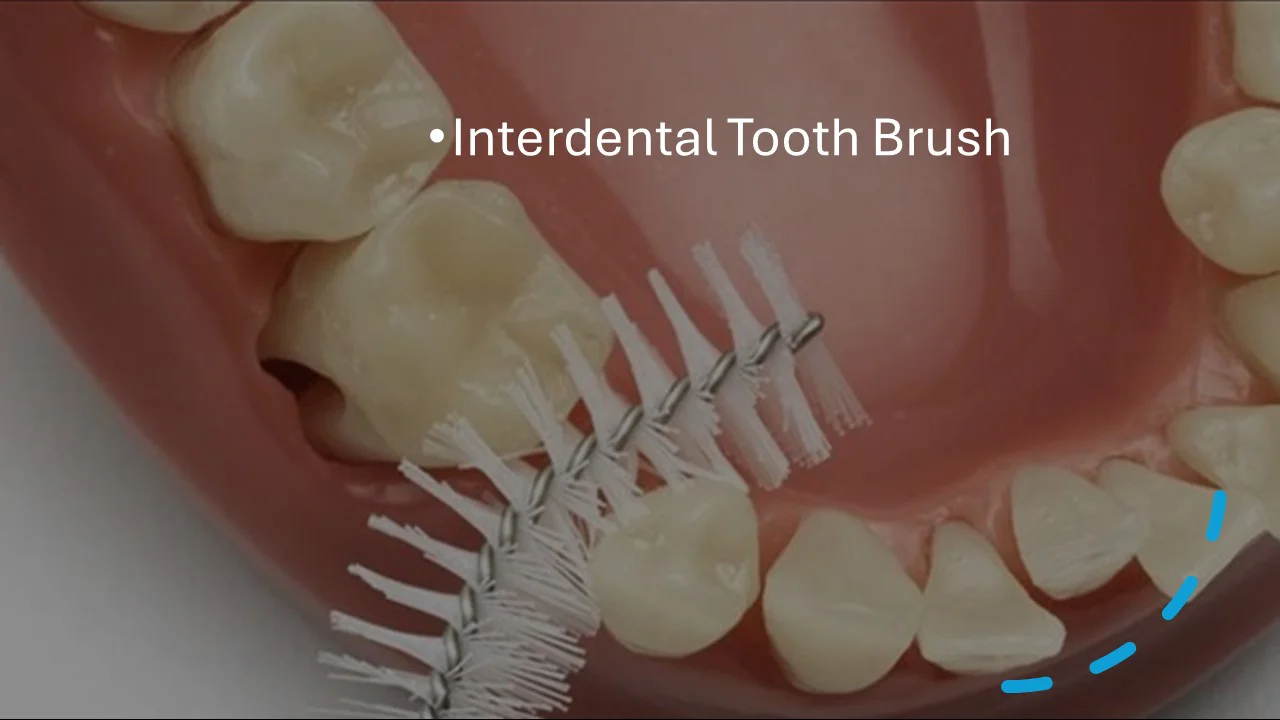
On the other hand, regular tooth brushing is insufficient to prevent gingivitis. It is essential to meticulously clean the regions that are inaccessible to the brush, particularly in the posterior areas, utilising interdental toothbrushes or floss. The pockets that form in these regions proliferate and result in the disease disseminating throughout the entire oral cavity.
In the prevention of periodontal disease, it is advisable to select toothpastes that demonstrate efficacy against dental caries rather than those with whitening properties. Moreover, using chewing gum that contains mouthwash and cytol three times a day for 20 minutes provides noteworthy benefits in the avoidance of these problems.
When untreated gum disorders continue to worsen over time, they pose serious risks. Let us now rank these hazards according to how significant they are at each stage of the illness.
- The patient's smile will be severely diminished, and the tooth roots will turn a discoloured shade as a result.
- The formation of plaque results in bad breath, which serves as an additional indicator of the hardening (petrification) of the plaques. It is possible to stop the disease from getting worse in this stage if it is managed properly.
- The more gum disease gets worse, the more cracks appear in the jawbone, which makes the jaw look worse.
- Due to intraoral bleeding, plaques disseminate to other areas of the body. Besides colonising kneecaps and heart valves, S. mutans bacteria can proliferate in the oral cavity, resulting in significant complications in these areas. Antibiotic therapy may not consistently yield successful outcomes in either situation.
Since the mouth is the first point of contact between the outside world and the rest of the body, taking care of one's teeth and gums is an absolute must for good health. Plaque puts you at risk, but remember that you are even more vulnerable if you are not scared of it.
For at least one day after peritoneal therapy, infection control measures must be strictly adhered to. Antibiotics are typically used to treat patients at this time. For a certain period of time, you should avoid smoking and drinking alcohol because the areas that have had plaque removed are more vulnerable to the buildup of bacteria.
To stop bacteria from growing again, dental hygiene should be prioritised following therapy. There are a lot of complaints regarding plaque formation following therapy. The patients' improper dental cleaning practices are the main cause of this. For this reason, it is essential to use dental floss and mouthwash.
The table below provides an overview of the most common prices for orthodontic treatments.
| Country | Treatment | Price | Currency |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Scaling & Root Planing | 300 | GBP |
| Bone Augmentation | 800 | GBP | |
| Anesthesia | 100 | GBP | |
| USA | Scaling & Root Planing | 400 | USD |
| Bone Augmentation | 1000 | USD | |
| Anesthesia | 150 | USD | |
| Germany | Scaling & Root Planing | 350 | EUR |
| Bone Augmentation | 900 | EUR | |
| Anesthesia | 120 | EUR | |
| Turkey | Scaling & Root Planing | 200 | USD |
| Bone Augmentation | 700 | USD | |
| Anesthesia | 50 | USD |
For the successful implementation of periodontic treatments, it is essential for the patient to possess healthy saliva. The pityalin enzymes present in saliva facilitate the breakdown of food residues within the oral cavity, whereas lysozyme enzymes are crucial for the eradication of microbial entities. In pregnant women and individuals with diabetes, these enzymes may be present in minimal quantities due to the elevated acidity levels in the oral cavity.
Patients with diabetes have slower wound healing, so periodontal treatments may increase the risk of microbial infection. For individuals with diabetes, it is recommended that the patient's HbA1c level be maintained below 6.5% to 7%, and that the fasting blood glucose level be reduced to below 130 mg/dL.
It is a prevalent misconception that periodontal disease does not manifest in individuals who engage in regular tooth brushing; but this claim is incorrect. Despite regular tooth brushing, the lack of dental floss and mouthwash use, as well as inadequate adherence to the two-minute brushing guideline, may increase the risk of periodontal disease.
Another common misconception is that the disease affects only the elderly. This is also another common misconception. In females, periodontal diseases often present at a young age due to factors such as increased oral acidity, especially during pregnancy.
What are the early signs of periodontal disease?
The first symptom of peirodontal disease is dark red gums. This is subsequently accompanied by haemorrhaging and oedema of the gingival tissues. Nonetheless, the initial development of dental plaque is associated with halitosis. Although halitosis is not a symptom of this disease, it serves as an initial indicator for early intervention.
How does plaque lead to gum disease?
Dental plaque is a biofilm composed of bacteria that adhere to salivary proteins and attach to the enamel of teeth. Consequently, the formation of plaque predominantly takes place in regions adjacent to the salivary glands. The process of plaque formation occurs within a time frame of 72 hours. During this time, the bacteria, which form a soft tissue, harden and adhere to the tooth surface, and once hardened, they cannot be removed from the mouth with oral hygiene.
What is the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis?
Gingivitis represents the initial stage of the disease, whereas periodontitis occurs when bacteria create pockets and advance to the roots of the teeth. In instances of periodontitis, there is a loss of bone density, which may result in the loosening of teeth.
Can gingivitis be reversed?
During the gingivitis stage, characterised by the formation of periodontal pockets measuring less than 4 mm, the condition is considered reversible. Nonetheless, if the disease has advanced to the periodontitis stage, surgical intervention is typically necessitated.
Is laser treatment for periodontal disease effective?
Laser treatment demonstrates significant efficacy when bacterial infiltration has not advanced beyond a depth of 6 to 7 cm, thereby yielding successful outcomes with minimal haemorrhaging. Nevertheless, manual cleaning is essential for the eradication of deep-seated bacteria.
What is involved in scaling and root planing?
In these treatments, the initial step involves determining the pocket depths and identifying the areas that require cleaning. Typically, the oral cavity is partitioned into two or four distinct sections, and the therapeutic intervention is administered independently for each section. Probes specifically designed for each region are utilised in the treatment process.
How can I prevent periodontal disease?
The timely intervention in periodontal diseases constitutes the most critical factor in the prevention of the disease. By initiating early action, it is possible to impede the progression of the disease to subsequent stages and to identify specific areas that require increased attention during the cleaning process.
Is regular flossing enough to prevent gum disease?
Flossing plays a crucial role in the prevention of periodontal diseases. Nevertheless, certain errors committed during the process of flossing may exacerbate the progression of periodontal diseases. The most prevalent error involves applying excessive pressure with dental floss, thereby displacing the gums towards the root of the tooth.
Can periodontal disease affect my overall health?
In periodontal diseases, the accumulation of bacteria within the oral cavity poses a risk of systemic dissemination due to bleeding or other impacts. Heart valves and knee joints are the two most critical anatomical regions in the body where plaque accumulation occurs.
What happens if I don’t treat gum disease?
Untreated periodontal diseases lead to tooth loss as a result of the natural development of the disease. But this is not the only downside. The disease can damage the jawbone and cause significant damage to the patient's facial aesthetics.
How long does it take to recover from periodontal treatment?
The primary concern following the treatment is the healing of the wounds in the affected areas and the mitigation of the risk of infection. In this regard, the patient should exercise considerable caution on the initial day. On the following day, the patient may resume his or her daily activities.
What should I avoid after gum surgery?
Following periodontal surgical interventions, it is advisable to refrain from the use of tobacco products and the consumption of alcoholic beverages. Moreover, to prevent undue pressure on the dental roots resulting from surgical intervention, it is advisable to avoid the consumption of hard foods.
Is periodontal treatment covered by insurance?
Periodontal treatments are not classified as cosmetic procedures and are typically eligible for coverage under insurance plans. Nevertheless, given the protracted onset of the disease in these conditions, it is prudent to examine the insurance stipulations.
How does smoking affect periodontal treatment?
It is advisable to refrain from smoking following periodontal treatment. In the absence of intervention, the opened gums may rapidly revert to their original configuration.
Are pregnant women at higher risk for gum disease?
During gestation, there is an increase in oral acidity, and complications such as xerostomia are frequently observed as a result of hormonal fluctuations. This elevates the risk of developing periodontal diseases during the course of pregnancy. Nevertheless, it is advisable for pregnant women to postpone treatment until after the lactation period, unless it is deemed absolutely necessary.
Can periodontal disease be cured?
All periodontal diseases can be effectively managed with prompt intervention. The deterioration of the patient's jawbone can be rectified through bone augmentation treatments in regions exhibiting bone resorption.
Is gum disease hereditary?
Genetic factors significantly contribute to the aetiology of periodontal disease. These factors are classified distinctly as periodontal diseases that are not attributable to plaque. Individuals with a familial history of certain conditions should recognise that periodontal disease may also increase their risk of developing similar health issues.
Timeline to your new smile.
A more beautiful version of your present smile.
Dental Health is our super and only one specialisation.
Dental & oral health is our passion. The goal is a less obvious, natural and more beautiful version of your current smile and oral health.
Bright smile.
Illuminate your world with a smile that shines bright and exudes confidence.
Confidence booster.
Unlock your true potential with a smile that boosts your confidence.
Pure & perfect.
Experience the pinnacle of dental perfection with avita dental treatments.









